Introduction
In recent years, advances in material science have revolutionized the field of facial prosthetics, offering patients a new lease on life with realistic and comfortable prostheses. Among the myriad of materials used, Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) has emerged as the material of choice in modern facial prosthetic applications.
This synthetic polymer, widely known for its flexibility, biocompatibility, and durability, plays a crucial role in enhancing the quality of life for individuals requiring facial reconstruction due to trauma, congenital defects, or diseases like cancer.
The evolution of facial prosthetics has been driven by the need for materials that not only replicate the appearance of natural skin but also provide the functional and emotional benefits necessary for patients to lead a normal life.
Polydimethylsiloxane, with its unique properties, meets these requirements more effectively than any other material available today. This blog post delves into why Polydimethylsiloxane reigns supreme in modern facial prosthetic applications and how it has transformed the landscape of facial reconstruction.
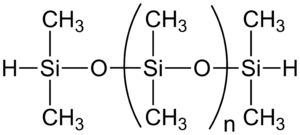
The Science Behind Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)
What is Polydimethylsiloxane?
Polydimethylsiloxane, commonly abbreviated as PDMS, is a silicone-based organic polymer known for its exceptional physical properties. It consists of a silicon-oxygen backbone with organic methyl groups attached to the silicon atoms, which contribute to its flexibility and resistance to environmental factors.
PDMS is characterized by its colorless, transparent appearance, making it ideal for applications that require visual discretion, such as facial prosthetics.
Key Properties of PDMS in Facial Prosthetics
The widespread adoption of Polydimethylsiloxane in modern facial prosthetic applications can be attributed to several key properties:
- Biocompatibility: PDMS is highly biocompatible, meaning it is well-tolerated by the human body without causing adverse reactions. This makes it a safe choice for long-term use in facial prosthetics, where the material is in constant contact with the skin and underlying tissues.
- Flexibility and Elasticity: The polymer’s inherent flexibility allows it to mimic the natural movement of facial skin, providing a realistic appearance and feel. Its elasticity ensures that the prosthesis can withstand repeated use without losing its shape or function.
- Durability: PDMS is resistant to environmental factors such as UV radiation, temperature extremes, and moisture, which are critical in maintaining the longevity of facial prosthetics. This durability reduces the need for frequent replacements, making it a cost-effective option for patients.
- Ease of Fabrication: PDMS can be easily molded and tinted to match the patient’s skin tone and texture, allowing for highly customized prosthetics that blend seamlessly with the surrounding tissue.
Advantages of PDMS Over Traditional Materials
Comparisons with Other Materials
Before the advent of Polydimethylsiloxane, materials such as latex, polyurethane, and acrylic resins were commonly used in facial prosthetics. However, these materials had significant limitations in terms of comfort, durability, and aesthetics.
For instance, latex, while flexible, can cause allergic reactions and deteriorates quickly with exposure to sunlight. Polyurethane, although durable, lacks the natural feel and appearance required for high-quality prosthetics.
In contrast, Polydimethylsiloxane offers a unique combination of properties that make it superior to these traditional materials in modern facial prosthetic applications. Its non-reactive nature ensures that it does not cause allergic reactions, and its stability under various environmental conditions extends the lifespan of the prosthesis.
Improved Patient Outcomes
The use of Polydimethylsiloxane in facial prosthetics has significantly improved patient outcomes. Patients report higher levels of comfort and satisfaction due to the material’s ability to mimic the natural look and feel of skin. The flexibility of PDMS allows for more natural facial expressions, which is crucial for social interactions and emotional well-being.
Additionally, the customizability of PDMS means that prosthetics can be tailored to match the patient’s exact skin tone and texture, resulting in a more lifelike appearance. This not only boosts the patient’s confidence but also reduces the psychological impact of facial disfigurement, leading to better overall quality of life.
Applications of Polydimethylsiloxane in Modern Facial Prosthetics
Trauma and Surgical Reconstruction
One of the most common applications of Polydimethylsiloxane in modern facial prosthetic applications is in the reconstruction of facial features following trauma or surgery. Patients who have undergone procedures such as tumor removal or injury repair often require prosthetics to restore the form and function of their faces. PDMS is ideal for these cases due to its ability to be precisely molded and colored to replicate the lost tissue.
Congenital Defects
Patients with congenital defects, such as cleft palate or craniofacial deformities, also benefit greatly from Polydimethylsiloxane prosthetics. These patients often require lifelong use of prosthetics, making the durability and biocompatibility of PDMS essential. The flexibility of PDMS allows for prosthetics that grow with the patient, reducing the need for frequent replacements as the patient ages.
Cosmetic Enhancements
In addition to medical applications, Polydimethylsiloxane is also used in cosmetic enhancements, such as non-surgical rhinoplasty and chin augmentation. The material’s ease of use and natural appearance make it a popular choice for patients seeking minor cosmetic adjustments without the need for invasive surgery.
Pediatric Applications
For pediatric patients, the safety and adaptability of Polydimethylsiloxane make it the material of choice. Children with facial deformities can benefit from PDMS prosthetics that are lightweight, comfortable, and capable of being adjusted as they grow. The non-toxic nature of PDMS ensures that it does not interfere with the child’s development or cause any long-term health issues.
Challenges and Future Directions
Current Limitations
Despite its many advantages, the use of Polydimethylsiloxane in modern facial prosthetic applications is not without challenges. One of the primary limitations is the cost of PDMS-based prosthetics, which can be prohibitively expensive for some patients.
Additionally, while PDMS is highly durable, it is not immune to wear and tear, and long-term use may still require occasional replacements or repairs.
Another challenge is the technical expertise required to fabricate PDMS prosthetics. The process of molding, coloring, and fitting the prosthetic requires specialized skills and equipment, which may not be readily available in all medical facilities.
Innovations on the Horizon
Research and development in the field of material science continue to explore ways to enhance the properties of Polydimethylsiloxane for modern facial prosthetic applications. One area of focus is improving the integration of PDMS with biological tissues, which could lead to prosthetics that not only mimic the appearance of skin but also promote healing and regeneration of the underlying tissue.
Additionally, advances in 3D printing technology are opening new possibilities for the customization of PDMS prosthetics. With 3D printing, prosthetics can be produced more quickly and at a lower cost, making them more accessible to a broader range of patients.
The Role of Patient-Centered Design
As the field of facial prosthetics continues to evolve, there is a growing emphasis on patient-centered design. This approach involves tailoring the prosthetic not only to the patient’s physical needs but also to their emotional and psychological well-being. Polydimethylsiloxane plays a crucial role in this approach, as its properties allow for the creation of prosthetics that are both functional and aesthetically pleasing.
By focusing on the patient’s overall experience, the future of modern facial prosthetic applications will likely see continued improvements in both the quality of the prosthetics and the satisfaction of the patients who use them.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Polydimethylsiloxane has undoubtedly established itself as the gold standard in modern facial prosthetic applications. Its unique combination of biocompatibility, flexibility, durability, and ease of customization makes it the ideal material for creating realistic and functional facial prosthetics.
As technology continues to advance, we can expect even more innovative uses of PDMS that will further enhance the quality of life for individuals requiring facial reconstruction.
The success of Polydimethylsiloxane in modern facial prosthetic applications is a testament to the importance of material science in improving patient outcomes. While challenges remain, ongoing research and development hold the promise of even greater advancements in the field.
We invite you to share your thoughts and experiences with Polydimethylsiloxane in the comments below. Whether you are a medical professional, a patient, or simply interested in the topic, your insights are valuable to the ongoing conversation about the future of facial prosthetics.





