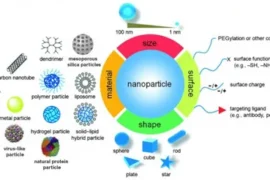
Introduction
Nanoformulations represent a promising frontier in drug delivery systems, where the development of efficient carriers can significantly improve the delivery, release, and efficacy of drugs. Polymers play a crucial role in the design and estimation of drugs in nanoformulations.
In drug delivery systems, particularly nanoformulations, the stability, release kinetics, and bioavailability of drugs can be significantly affected by the polymers used in their formulation. Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA), Polyvinyl Pyrrolidone (PVP), Chitosan, and Carboxymethyl Cellulose (CMC) are commonly used polymers in the pharmaceutical industry. These polymers interact with drugs, forming matrices that encapsulate or bind the drug molecules, affecting drug release, bioavailability, and, consequently, drug estimation.
Nanoformulations, which involve drug particles sized between 1 and 100 nanometers, offer several advantages, including enhanced solubility, improved bioavailability, and targeted drug delivery. However, the success of these formulations depends largely on the choice of polymers. PVA, PVP, Chitosan, and CMC each bring unique properties to the table that influence the overall efficacy and precision of drug estimation in nanoformulations. This blog will examine the contributions of these polymers in enhancing drug performance and accuracy in dosage estimation.
In this article, we will explore in detail the role of Polyvinyl Alcohol, Polyvinyl Pyrrolidone, Chitosan, and Carboxymethyl Cellulose in drug estimation within nanoformulations.

1. Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA) in Drug Estimation
Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA) is a widely used synthetic polymer in pharmaceutical nanoformulations due to its excellent film-forming properties, high solubility in water, and biocompatibility. In drug nanoformulations, PVA serves as a stabilizer and emulsifying agent, ensuring uniform drug distribution within the formulation. One of the significant challenges in nanoformulation is preventing drug aggregation, and PVA’s stabilizing role is critical in ensuring that drug particles remain evenly dispersed.
PVA’s Role in Drug Release
PVA creates a semi-permeable membrane around drug nanoparticles, controlling the rate at which the drug is released into the bloodstream. This controlled release is vital for ensuring consistent drug bioavailability over time, which directly affects the drug’s therapeutic efficacy. Furthermore, PVA influences the degradation rate of nanoformulations, helping prolong the drug’s presence in the system.
Impact on Drug Estimation
The presence of PVA in nanoformulations can complicate drug estimation because its interaction with drug molecules might mask certain drug characteristics during analytical procedures. Analytical methods such as UV-Vis spectroscopy, High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC), and others might require modifications to accurately estimate drug concentration due to PVA’s interference. However, PVA’s ability to enhance drug solubility and stability often outweighs these challenges, as it ensures more consistent drug delivery profiles.
When considering drug estimation in nanoformulations, Polyvinyl Alcohol is essential for improving the stability of formulations and controlling the release kinetics of the active ingredients.
2. Polyvinyl Pyrrolidone (PVP) in Drug Nanoformulations
Polyvinyl Pyrrolidone (PVP) is another versatile polymer used in pharmaceutical applications due to its solubility in both water and organic solvents, biocompatibility, and ability to form stable colloidal dispersions. PVP is often used in the stabilization of drug nanoparticles and improving drug solubility in nanoformulations.
PVP’s Role in Drug Solubility and Stability
One of the key roles of PVP in nanoformulations is its ability to enhance drug solubility. Many drugs, particularly hydrophobic drugs, suffer from poor solubility, which directly impacts their bioavailability and therapeutic efficacy. PVP forms hydrogen bonds with the drug molecules, increasing their solubility and, consequently, their bioavailability. Additionally, PVP prevents drug crystallization, maintaining the drugs in an amorphous state, which is more readily absorbed by the body.
Impact on Drug Estimation
The use of PVP in nanoformulations can affect drug estimation due to its ability to form complexes with the drug molecules. These complexes can alter the drug’s absorption characteristics and may lead to inaccuracies in drug quantification methods like UV-Vis spectroscopy and HPLC. However, these effects can be accounted for by calibrating the analytical techniques used in drug estimation.
By enhancing drug solubility and stability, Polyvinyl Pyrrolidone plays a pivotal role in improving the bioavailability and therapeutic efficacy of drugs in nanoformulations, while requiring careful consideration in drug estimation processes.
3. Chitosan in Drug Nanoformulations
Chitosan, a natural polymer derived from chitin, has garnered significant attention in drug delivery systems due to its biocompatibility, biodegradability, and non-toxic nature. It is especially valuable in nanoformulations for its mucoadhesive properties and its ability to enhance the permeability of drug molecules across biological membranes.
Chitosan’s Role in Drug Delivery
One of the most notable characteristics of Chitosan is its ability to enhance the absorption of drugs by increasing their permeability across epithelial barriers, making it particularly useful for drugs that need to be absorbed through mucosal surfaces like the gastrointestinal tract.
Additionally, Chitosan nanoparticles can encapsulate both hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs, providing a versatile platform for drug delivery. Chitosan-based nanoformulations can also offer sustained release, ensuring that the drug is released gradually over time, which is crucial for maintaining therapeutic levels of the drug in the bloodstream.
Impact on Drug Estimation
Chitosan’s interaction with drug molecules can complicate drug estimation. In particular, its mucoadhesive properties and the ability to form ionic bonds with negatively charged drug molecules can lead to alterations in drug absorption profiles, requiring advanced analytical techniques to accurately estimate the drug concentration in nanoformulations. Methods such as HPLC may need to be adjusted to account for the polymer’s interaction with the drug.
For drug delivery via nanoformulations, Chitosan is a highly effective polymer that enhances drug permeability and stability, though it introduces complexities in the drug estimation process due to its strong binding properties.
4. Carboxymethyl Cellulose (CMC) in Nanoformulations
Carboxymethyl Cellulose (CMC) is a cellulose derivative that is widely used in pharmaceutical formulations for its hydrophilic and gelling properties. In nanoformulations, CMC serves as a stabilizer and a drug carrier, enhancing the solubility and bioavailability of poorly soluble drugs.
CMC’s Role in Drug Solubility and Stability
CMC is particularly useful in enhancing the solubility of hydrophobic drugs, forming stable dispersions in aqueous solutions. Its ability to form a gel-like structure helps in the controlled release of drugs, making it ideal for sustained-release formulations. Furthermore, CMC can protect drug molecules from degradation by encapsulating them in a hydrophilic matrix, ensuring prolonged drug stability.
Impact on Drug Estimation
The gelling properties of CMC can present challenges in drug estimation, particularly in methods that rely on the free diffusion of drug molecules, such as dialysis or certain chromatographic techniques.
The encapsulation of drugs within a CMC matrix may necessitate more advanced or modified analytical techniques to accurately quantify drug concentration. Additionally, the hydrophilic nature of CMC can interfere with some spectrophotometric methods, requiring calibration to ensure accurate drug estimation.
Carboxymethyl Cellulose is a valuable polymer in drug nanoformulations for improving drug solubility and stability, though it may require specialized approaches in drug estimation to account for its unique properties.
Conclusion
In the world of drug nanoformulations, polymers like Polyvinyl Alcohol (PVA), Polyvinyl Pyrrolidone (PVP), Chitosan, and Carboxymethyl Cellulose (CMC) play crucial roles in determining the stability, solubility, bioavailability, and release profiles of drugs. Each polymer brings unique advantages, from enhancing drug permeability and solubility to stabilizing drug nanoparticles and providing sustained drug release.
However, these polymers also introduce challenges in drug estimation, as their interactions with drug molecules can affect analytical measurements. Therefore, it is crucial for researchers and pharmaceutical developers to carefully choose and calibrate their drug estimation methods when working with these polymers in nanoformulations.
If you have any thoughts or questions about How Polyvinyl Alcohol, Polyvinyl Pyrrolidone, Chitosan, Carboxymethyl Cellulose, Drug, and Nanoformulations, feel free to leave a comment below!